Operational amplifiers are very important components in analog circuits. They can form various circuits such as amplification, addition, subtraction, and conversion, and are widely used in circuit design. So, if the circuit is abnormal, how should we check whether it is the cause of the damage to the operational amplifier? That is to use the “virtual short” and “virtual break” of the op-amp to analyze the circuit, and then combine some small skills to judge. Next, let us first understand what is “virtual short” and “false break”.
Virtual short
Virtual short means that under ideal conditions, the potentials of the two input terminals are equal, so that the two input terminals can be regarded as short-circuited together, but in fact there is no short-circuit, which is called “virtual short”. A necessary condition for virtual short is that the op amp introduces deep negative feedback.
Due to the large voltage amplification factor of the operational amplifier, the open-loop voltage amplification factor of general-purpose operational amplifiers is above 80 dB. The output voltage of the op amp is limited, generally between 10 V and 14 V. Therefore, the differential mode input voltage of the op amp is less than 1 mV, and the two input terminals are approximately equal potential, which is equivalent to “short circuit”. The greater the magnification of the open-loop voltage, the closer the potentials of the two input terminals are to the same.
False break
A virtual break is when, ideally, zero current flows into the input of an integrated op amp. This is due to the infinite input resistance of an ideal op amp, as if there was an open circuit between the two inputs of the op amp. But in fact there is no open circuit, which is called “virtual break”.
Because the differential mode input resistance of the operational amplifier is very large, the input resistance of general-purpose operational amplifiers is more than 1MΩ. Therefore, the current flowing into the input terminal of the op amp is often less than 1uA, which is much smaller than the current of the circuit outside the input terminal. Therefore, the two input terminals of the op amp can usually be regarded as an open circuit, and the greater the input resistance, the closer the two input terminals are to an open circuit.
Example analysis
As shown in Figure 1, it is a common inverse proportional operational amplifier circuit. The method of virtual short and virtual break is used to analyze the circuit below.
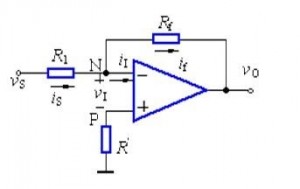
In the inverting amplifier circuit, the signal voltage is added to the inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier through the resistor R1, and the output voltage Vo is fed back to the inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier through the feedback resistor Rf, forming a voltage parallel negative feedback amplifier circuit.
The non-inverting terminal of the op amp is grounded equal to 0V, and the inverting terminal and the non-inverting terminal are imaginary short, so it is also 0V. The input resistance of the inverting input terminal is very high, and there is almost no current injection and outflow, so R1 and Rf are equivalent to series connection, because the current flowing through each component in a series circuit is equal, that is, flowing through R1 The current is equal to the current flowing through Rf.
According to Ohm’s law, we can get:
Is= (Vs- V-)/R1 …………a
If= (V- – Vo)/Rf ……b
V- = V+ = 0 ……………… c
Is = If ……………………d
After solving, it is possible that Vo== (-Rf/R1)*Vi
After understanding the principle of virtual short and virtual break, we can use it to judge the quality of the device in the practical op amp circuit. According to the principle of the virtual short of the amplifier, if the op amp works linearly, the voltages at the non-inverting input terminal and the inverting input terminal must be equal, even if there is a difference, it is still at the mv level. Of course, in some high input impedance circuits, the internal resistance of the multimeter will affect the voltage test a little, but generally it will not exceed 0.2V. If there is a difference of more than 0.5V, the amplifier must be broken!
In many instruments and meters, there are integrated operational amplifiers for small signal amplification, which are more fragile than other integrated blocks and components, so being able to quickly judge their quality can be said to be a shortcut for instrument repair. Many of the integrated blocks in more complex instruments and meters are directly welded on the printed circuit board, the circuit board is inserted into the socket, and the distance between the circuit boards is also very small. It is difficult to measure the voltage directly. Some simple and practical methods for judging integrated operational amplifier blocks are proposed below.
Модуль удаленного ввода-вывода
- Touch the temperature of the integrated op amp block by hand after power on for a period of time. If the temperature is greater than 50℃, it should be suspected whether it is damaged.
- If possible, measure the DC current, which should be within a few milliamps. Otherwise it is damaged.
- If the integrated operational amplifier has a single operational amplifier and several operational amplifiers combined, you should be familiar with its power supply and input and output pins. This also has certain rules to find and find the relevant manuals to know. The resistance between the input pins of the integrated operational amplifier should be relatively large (generally greater than 10 MΩ). When the measured value is small, observe the diode with infinite value at the input end, otherwise it will be damaged.

